Native Apps, Web Apps or Hybrid Apps – Know The Difference

Basically, mobile apps have three types of development processes – Native Apps, Web Apps, Hybrid Apps. All three have their terms of consideration like budget, timeline, technology considered by a business. In this blog, we will discuss each of them and their comparison to assist the businesses to rectify their benefits. But before that, let us know some of the basics of an app and comparative statistics.
Smartphone applications have expedited lifestyles that have entered the not-so-distant past. It’s been more than two decades that the application market has been diversified. Play Store and App Store grant numerous apps to be stored and installed. The graph shown below shows how many applications were floating in the Play Store each month in the previous years. It is in the thousands, which is quite a contender.
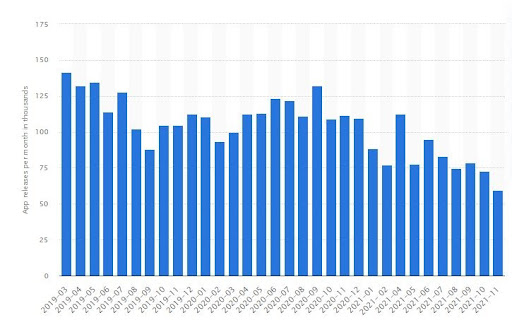
Source: (Statista)
Businesses are finding applications as an ultimate idea to offer resources. They are choosing apps to interact with the consumers. For this purpose, they have been finding their major concern, which is to select how the application is crafted. Also, they are important as we have seen to fight in the most competitive field. Businesses have to figure which blooming process will be apt for the apps to proffer the services, finding potential customers and a mass of end-users they are discovering.
We will scrutinize the foremost area of interest for mobile apps for any industry: an Android Vs. iOS app.
Android Vs. iOS Apps
First, let us acknowledge the distinction between the Android system and the iOS system. These are the 2 widely used operating systems to run smart apps. Google prospers Android, also partly an open-source run, entirely customizable, and Linux-based system. While iOS is originated by Apple and is congenial with only Apple’s devices like iPhone, Mac, iPad.
Android is the preferred operating system globally. Here is the chart describing the smartphone market worldwide. Android contributes 73%, holding the biggest share, in June 2021.(add source) However, its contribution has always been the widest. When it is joined with Apple’s iOS, it contributes 99% of the universal industry of the OS.
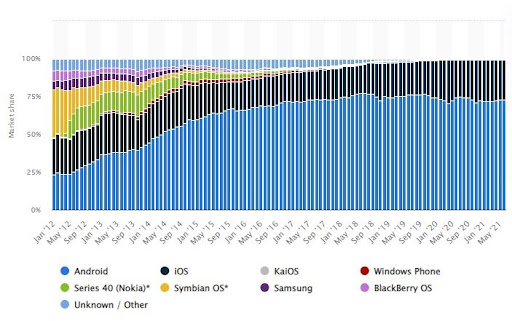
Source: (Statista)
Android is wielded on the devices of multiple companies. However, iOS, as mentioned, sticks to their own smart devices. On a different side, Android has an organized store with colossal apps. Moreover, its widgets are more useful in contrast with iOS.
We have endured the basics; let’s move to our major subjects – native, web apps, and hybrid, one by one.
What are Native Apps?
Native apps are smart applications that are amicable with particular devices or apparatus. These apps are depicted to drive in a particular operating system and take the most strengths of the new-fangled characteristics and tech stack. Native apps get quick access to specific OS’s standard characteristics like media, microphone, push notifications, etc. Its data storage is in the specific resource or cloud storage which is remote storage.
How are Native Apps Developed?
Native apps use separate technologies in development for particular devices or operating systems. For example, Objective-C and Swift are drawn on for native iOS and Kotlin or Java for native Android. These are crafted for certain devices that work quicker and give efficient staging. Native apps bring into play their own Integrated Development Environment (IDE). In essence, Android Studio is Android’s Standard Development Kit (SDK), and Xcode is iOS’s SDK.
Advantages of Native Apps
- Its apps give an elite performance
- It easily adopts the workability of the device
- Application matched particular mobile’s UI UX effortlessly
- They are braced by various app stores and marketplaces
- Apps are versatile and can be tailored to source management with various tools available.
Disadvantages of Native Apps
- Android and iOS have separate codebases, so they need to function on different codebases.
- Developing native apps is time-consuming as distinguished development is required for versions.
- As native apps are set up individually for different operating systems, they cost higher as different teams and resources.
What are Web Apps?
A website application, widely known as web apps, functions in browsers over the internet. Or it could be said as if it is software assembled with web-based technology. It needs three services for its working. A web server has to handle the task from the client-side, an app server to enforce the assignment requested, and a database to store information.
How are Web Apps Developed?
Web apps are erected with Javascript, CSS, and HTML5. Templates and substructures are assembled using Angular, React, and Vue.js. Node.js is utilized for the backend. For databases, MongoDB is preferred. After the advent of HTML5, web apps are explored more for their use cases. This doesn’t rely on the operating system they work with.
Advantages of Web Apps
- Have a unique codebase as it operates in any operating system
- Require no installation as it operates within a browsers
- Simple to develop in comparison to other apps
- Updates automatically, unlike other types
- It doesn’t need store approval as operated in the browsers.
Disadvantages of Web Apps
- Works only with a network like an internet
- Are comparatively redundant
- Needs no stores and therefore has higher search frictions
- Costlier to maintain
Web Apps and Websites
Website and web apps’ subjective discrepancy is that web apps are communal; they give responses to consumers’ activity. A website is only a one-way or informational citation for the consumers. Nevertheless, combinational web panels combine static and communicable responses for an enhanced use case, serving the purposes in a better way.
Progressive Web Apps
Web apps are not much interactive and lack a few of the important aspects of being an app. Therefore the development of progressive web apps came into existence. With the integrations of the interactive features and focussing on the progressive enhancement to deliver the best possible experience. It develops richer capabilities as a web app compared to the normal web app.
However, PWAs are not an alternative to apps as they don’t work sufficiently in both Android and iOS. They lack functionality in iOS and work deliberately. Since a progressive website app is a web app, it is not downloaded from a store. Its compatibility is still under development to achieve the motive of a native app.
Mobile Apps Vs. Web Apps
Mobile apps are primer to web apps as they lack many features. Nevertheless, the major effects of both are separate in their frequent usability. A web app is used for gaining desktop users, gaining organic traffic, assigning convenience to potential consumers but is not a better fit for chronic use. In that case, smartphone apps are determined to a specific purpose without distractions. In different sentences, apps provide direct interaction for the app’s end-user. They could even be used without the internet, unlike web apps.
What are Hybrid Apps?
As the name suggests, hybrid apps are the hybrid of native and web apps, consisting of characteristics of both of them. The app is integrated with all the qualities of the web app, which can be found in the store and installed in the form of an app. When users install the app in the device’s local storage, it can access all features that a browser provides. It has the major perk of accommodating its code to multiple platforms.
How are Hybrid Apps Developed?
Hybrid apps are developed with a single codebase for multiple devices compatibility. It is developed using a mobile Webview context and web developing tech stack. When it is viewed on mobile, it shows the web content. It uses the application wrapper solution that enlarges the use of web browsers afar constraints and enters the full suite of competency of a mobile application.
In between the source code and a device, there is an extra layer that helps conduct the working of the hybrid apps in the particular device, although it slows down the working of the app.
Advantages of Hybrid Apps
- They are crafted rapidly as unique code for each OS.
- They are comparatively cost-effective.
- It has an abundant reach as it can acquire web and app audiences.
- Flexible to tailored to elite suit other platforms
Disadvantages of Hybrid Apps
- App has sedate performance than native apps
- Certainly, hybrid apps do not integrate the most compounded workability.
- Absence of 3D support for the elements in the app
Native, Web or Hybrid Apps – Select the Best App For Business
So far, we have discussed all these ways of app development. Each has its gains and losses, ensuring their aspects at best. Their app type or app development concerns some fundamentals from a business perspective, our forthcoming discussion.
Brass Tracks of Application Development for a Business
Operating System of Mobile Users
A business’s motive is to gain a huge customer base that affects while selecting a developing process for a mobile app. For example, they have to opt for the consumer base of Android, iOS or both. As the statistics showed priorly, Android has a vast customer base, as we have gone through. Accordingly, a business has to decide its development type.
Price and Time to Build The Apps
As talked through the blog, each development has distinct strengths and weaknesses, which also includes dissimilar costing structure and timeline. So, if development prices are limited, businesses should have the choices that imply their investment plans. Estimation of budget and development can also help to choose the one wisely.
Technology Used for Business
The tech stack assists for app building is also fundamental for a business. Nevertheless, a business is not aware of the technology for their best outcomes. In that case, relying on an application development company to choose the aptest ones is beneficial. In that case, it would be even effortless for a business to consider forthcoming requirements.
Final Notes on Native, Web and Hybrid Apps
Native apps, web apps, and hybrid apps are thoroughly argued in the blogs. Different aspects like time, budget, audience base, and technology separate them. A business could take the edge of choosing one of them. Though there is no eccentric solution, these aspects and the business’s end goal would help choose a seek-through. Getting a technological partner can follow the right hail for your business to get the right solution.

